CRA COMPLIANCE
Prepare for EU’s Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) compliance with confidence. Meroi Security’s expert compliance services ensure your products meet the stringent cybersecurity requirements, safeguarding your business, customers, and market access in the European Union.
Understanding the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA)
The CRA, formally Regulation (EU) 2024/2847, is a landmark EU regulation introducing mandatory cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements (PDEs) placed on the EU market. Enacted on December 10, 2024, with main obligations applying from December 11, 2027, the CRA addresses escalating cyber threats by ensuring hardware and software products are secure throughout their lifecycle. It complements the CE marking framework and aligns with the NIS2 Directive, filling gaps in existing EU legislation that previously did not cover the cybersecurity of non-embedded software. Reporting obligations for vulnerabilities and incidents begin September 11, 2026.

Key requirements of the Cyber Resilience Act
The CRA outlines four main objectives to ensure cybersecurity across the product lifecycle:
- Cybersecurity by Design: Products must minimize attack surfaces and ensure secure configurations.
- Coherent Cybersecurity Framework: Align with standards like ETSI EN 303 645, IEC 62443, and EUCC.
- Transparency: Provide security information and secure data removal/transfer options.
- Secure Usage: Enable secure use THROUGH timely updates and clear instructions.
Practical requirements include:
- Products must be free of known exploitable vulnerabilities at market entry.
- Maintain a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) using formats like SPDX or CycloneDX.
- Regular security tests and reviews.
- Coordinated vulnerability disclosure policies aligned with NIST SP 800-61.
- Timely, free security updates with advisory messages.
- Incident reporting to ENISA within 24 hours.
- CE Marking: Compliance is mandatory, with documentation retained for 10 years.
Scope of the Cyber Resilience Act
The CRA applies to all Products with Digital Elements (PDEs) that have a direct or indirect logical or physical connection to a device or network, as outlined in Annex I. This includes:
- Hardware: IoT devices (e.g., smart cameras, fridges, TVs, toys), embedded systems (e.g., industrial controllers, sensors).
- Software: Operating systems, cloud-based services, and certain SaaS solutions if classified as remote data processing solutions.
- Supply Chain Actors: Manufacturers, importers, distributors, and resellers, with obligations varying by role.
- Exclusions: Products covered by sector-specific EU regulations, such as medical devices, motor vehicles, civil aviation systems, marine equipment, and products for national security or defense.
- Open-Source Software: Excluded unless part of a commercial activity.
- High-Risk AI Systems: Covered to align with the EU AI Act.
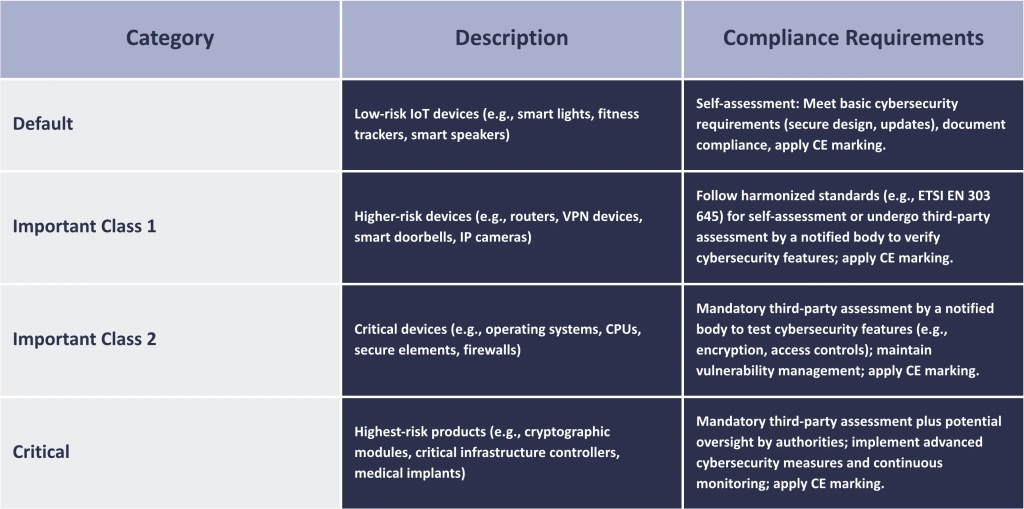
Product classes under CRA Compliance
The CRA categorizes PDEs based on cybersecurity risk, as detailed in Annex III, determining conformity assessment requirements:
- Default Category: Consumer-grade products requiring self-assessment.
- Important Products:
- Class I: Lower-risk critical products (e.g., password managers, routers). Conformity assessment via self-assessment or third-party review using harmonized standards or European cybersecurity certification schemes (EUCC).
- Class II: Higher-risk products (e.g., firewalls, hypervisors). Mandatory third-party conformity assessment.
- Critical Products: Essential for secure operations (e.g., smartcards, hardware security modules). Mandatory third-party assessments and EUCC certification at least at the “substantial” level.
What is CE Marking?
CE marking is a certification mark indicating that a product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards, allowing it to be placed on the EU market. Under the CRA, CE marking requires compliance with cybersecurity requirements outlined in Annex I. Manufacturers must demonstrate conformity through self-assessment or third-party assessments, affixing the CE mark to signify compliance. Learn more about CE marking.

What are Harmonized Standards and their integration with the CRA?
Harmonized standards are technical specifications developed by European standardization organizations and adopted by the EU to ensure consistent compliance with regulations like the CRA. These standards, listed in the Official Journal of the EU, provide a presumption of conformity with CRA requirements when followed. For example, ETSI EN 303 645 for IoT devices and IEC 62443 for industrial systems align with CRA’s cybersecurity objectives. The CRA integrates harmonized standards to streamline compliance, reduce costs, and ensure interoperability.
Key differences between Self-Assessment and Third-Party Assessment
Self-assessment is when a company evaluates its own products, processes, or systems to determine if they meet specific standards or regulations. This is conducted internally, using the company’s own staff, resources, or tools, without external involvement.
- Use Case: In the context of the CRA, self-assessment is permitted for default category products—like consumer-grade IoT devices (e.g., smart speakers or fitness trackers)—which are considered lower risk.
- Advantages:
- Faster, as it doesn’t rely on scheduling with external parties.
- Less costly, since it avoids fees for external auditors or certification bodies.
- Disadvantages:
- Less rigorous, as it depends on the company’s own expertise and diligence.
- Potentially biased, as the company is “grading its own homework,” which may lead to overlooked issues or lack of objectivity
Third-party assessment involves an external, independent entity—such as an auditor, certification body, or notified body—evaluating a company’s products or processes for compliance. The external entity performs an in-depth review, which may include audits, testing, or certification, to verify adherence to standards.
- Use Case: Under the CRA, third-party assessments are required for important products (Class II) and critical products (e.g., firewalls, smartcards, hardware security modules), which carry higher cybersecurity risks.
- Advantages:
- More objective, as it’s conducted by an impartial party with no stake in the outcome.
- More credible and thorough, offering greater assurance to regulators, customers, and stakeholders.
- Disadvantages:
- More time-consuming, due to coordination with external entities and detailed review processes.
- More expensive, as it involves paying for professional services.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with CRA
Non-compliance carries severe penalties under Article 54 of the CRA:
- Fines: Up to €15 million or 2.5% of global annual turnover for core breaches.
- Market Restrictions: Products may be prohibited, withdrawn, or recalled.
- Corrective Actions: Authorities may mandate security measures or recalls.
- Additional Risks: Reputational damage and liability under related laws like GDPR.
Comparison with other Cybersecurity Regulations and Standards
The CRA complements other EU regulations and standards, as detailed in ENISA’s CRA Standards Mapping:
- NIS2 Directive: Focuses on critical infrastructure cybersecurity.
- GDPR: Aligns with data protection requirements.
- DORA: Targets financial sector cybersecurity.
- ETSI EN 303 645: IoT-specific standard.
- IEC 62443: Focuses on industrial systems.
- ISO/IEC 27001/27002: High-level security management guidelines.
- EUCC: Mandatory for critical products.
Gaps: Standards lack detailed guidance on SBOMs and disclosure timelines.
Why choose Meroi Security for CRA Compliance?
Meroi Security offers unique advantages for achieving CRA compliance:
- Specialized Expertise: In-depth knowledge of CRA, NIS2, GDPR, etc.
- Tailored solution: we work with a small number of client, ensuring total dedication and customisation of our offerings.
- Hands-On Approach: Implementing technical controls aligned with standards.
- End-to-End Support: From gap analysis to post-market compliance.
- Scalability and Resilience: Enhancing long-term security and trust.
- Core Values: Integrity and performance in service delivery.
How Meroi Security helps you achieve CRA Compliance
We provide tailored services to meet CRA requirements:
- Gap Analysis: Identify compliance gaps against Annex I of the CRA.
- Resilient Lifecycle: Integrate cybersecurity into development processes.
- Implementation Support: Develop SBOMs, disclosure policies, and incident reporting.
- Supply Chain Compliance: Audit and guide partners.
- Documentation: Prepare technical documentation for CE marking.
- Training: Equip teams with compliance and threat response skills.
Contact us today for a free CRA Compliance consultation
With penalties up to €15 million, compliance is critical. Partner with Meroi Security to meet EU standards and avoid market exclusion.
Contact us at [email protected]
